-
Services
Services
Services--
- Document Management
- Carton Management & Storage
- File management
- File Room Solution
- Media storage
- Vault storage
- Insight
- About Us About Us
- Locations
- Customer Centre
Understanding Information Lifecycle Management (ILM): Definition & Insights
In today’s data-driven world, organisations are constantly grappling with the challenge of managing vast amounts of information effectively. This is where Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) comes into play, offering a comprehensive approach to overseeing data throughout its lifecycle.
We will delve into the definition, benefits, and best practices of ILM, providing valuable insights for businesses looking to optimise their data management strategies.
What is Information Lifecycle Management (ILM)?
Information Lifecycle Management, commonly referred to as ILM, and we will be using this acronym throughout this insight. ILM is a comprehensive approach to managing an organisation’s data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to deletion.
It encompasses a set of strategies, processes, and tools designed to store data, protect it, and ensure its availability while optimising storage resources and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. Unlike traditional data management approaches, ILM takes into account the changing value of information over time and applies appropriate management policies based on the data’s business value and legal or regulatory obligations.
How does ILM differ from traditional data management?
Traditional data management often treats all data equally, storing it in a single repository without considering its varying importance or relevance over time. In contrast, ILM recognises that the value of information changes throughout its lifecycle.
It implements intelligent data management practices that align with these changes, ensuring that data is stored, accessed, and protected according to its current value and relevance to the organisation. This dynamic approach allows for more efficient use of storage resources and better alignment with business needs.
Here’s a comprehensive comparison between information management vs data management.
Why is ILM important for businesses and organisations?
In an era where data is often referred to as the new oil, effective management of information assets has become crucial for business success. ILM helps organisations handle the exponential growth of data, both structured and unstructured, by providing a framework to manage information based on its value and relevance.
It enables businesses to comply with increasingly complex regulatory requirements, reduce storage costs, improve data accessibility, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Moreover, ILM plays a vital role in data protection and security, helping businesses safeguard sensitive information and mitigate the risks of data loss or breaches.
What are the key components of an ILM strategy?
An effective ILM strategy comprises several key components that work together to manage data throughout its lifecycle. These include data classification, which involves categorising data based on its importance and sensitivity; storage tiering, which allocates data to appropriate storage mediums based on its value and access requirements; data retention policies, which define how long data should be kept and when it should be archived or deleted; and data protection measures, which ensure the security and integrity of information assets. Additionally, data governance plays a crucial role in ILM, providing the overarching framework for how data should be managed, accessed, and used within the organisation.
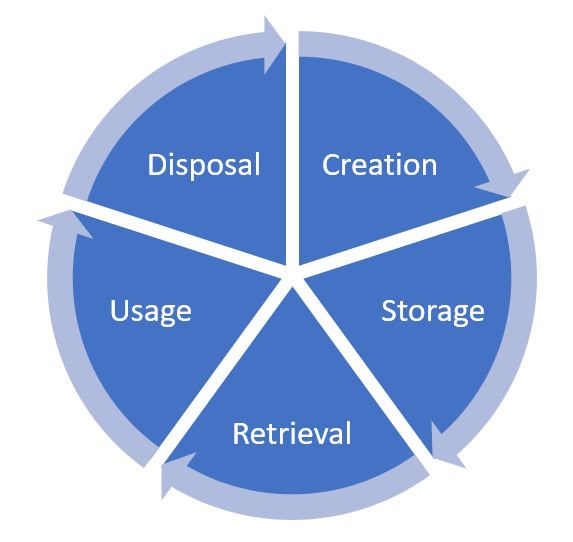
What are the phases of Information Lifecycle Management?
The Information Lifecycle Management process typically consists of several distinct phases, each addressing different aspects of data management throughout its lifecycle. Understanding these phases is crucial for implementing an effective ILM strategy that aligns with an organisation’s data management needs and business objectives.
The phases of Information Lifecycle Management typically include:
- Creation/Capture
- Storage
- Usage
- Archiving
- Retention
- Disposal/Destruction
- Compliance and Governance
How does data creation fit into the ILM process?
The data creation phase marks the beginning of the information lifecycle. During this stage, new data is generated or acquired by the organisation through various means, such as user input, system logs, or external sources. ILM strategies should address this phase by implementing proper data classification and metadata tagging at the point of creation.
This ensures that newly created data is immediately categorised and assigned appropriate management policies based on its content, sensitivity, and potential business value. By starting the ILM process at the creation phase, organisations can more effectively manage data from the outset, reducing the risk of misclassification or improper handling later in its lifecycle.
What happens during the data storage and usage phase?
The storage and usage phase is where data is actively utilised and maintained within the organisation’s storage systems. During this phase, ILM plays a crucial role in ensuring that data is stored efficiently and remains easily accessible to authorised users. This involves implementing tiered storage solutions, where data is allocated to different storage tiers based on its current value and access requirements.
Frequently accessed or high-value data may be stored on fast, premium storage systems, while less critical or infrequently accessed data can be moved to lower-cost storage options. ILM also ensures that appropriate data protection measures are in place during this phase, including backup and recovery processes, access controls, and encryption for sensitive information.
When and how should data be archived or deleted?
As data ages and its business value diminishes, it enters the archival or deletion phase of its lifecycle. ILM strategies should include clear policies for determining when data should be archived or securely deleted. Archiving involves moving data that is no longer actively used but must be retained for legal or historical purposes to long-term, cost-effective storage solutions.
This frees up primary storage resources while ensuring that the data remains accessible if needed. For data that has become obsolete or is no longer required, ILM policies should specify secure deletion procedures to ensure that sensitive information is completely and irrevocably removed from all storage systems. These processes must comply with data retention regulations and consider the potential future value of the information before permanent deletion.
Managing Information from Creation to Retention
Effective information management requires a holistic approach that covers every stage of the information lifecycle, from creation to retention.
By implementing best practices for information storage, access, and eventual disposal, we help organizations streamline operations, maintain compliance, and reduce risks.
What are the benefits of implementing Information Lifecycle Management?
Implementing a robust Information Lifecycle Management strategy offers numerous benefits to organisations, ranging from improved operational efficiency to enhanced compliance and cost savings.
By adopting ILM practices, businesses can optimise their data management processes and derive greater value from their information assets.
How does ILM improve data storage efficiency?
One of the primary benefits of ILM is its ability to significantly improve data storage efficiency. By implementing tiered storage strategies, organisations can optimise their storage resources, ensuring that data is stored on the most appropriate medium based on its current value and access requirements. This approach allows businesses to make better use of high-performance, more expensive storage for critical data while leveraging lower-cost options for less frequently accessed information.
Additionally, ILM helps identify and remove redundant, obsolete, or trivial data, freeing up valuable storage space and reducing the overall storage footprint. This improved efficiency not only leads to cost savings but also enhances system performance and data accessibility.
Can ILM help with regulatory compliance?
In today’s complex regulatory environment, compliance with data protection and retention laws is a critical concern for many organisations. ILM plays a crucial role in helping businesses meet these compliance requirements by providing a structured approach to managing data throughout its lifecycle.
By implementing clear data retention policies and ensuring proper data classification, ILM enables organisations to demonstrate compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards. It also facilitates the implementation of data governance practices, ensuring that sensitive information is handled appropriately and that data can be easily located and retrieved when needed for audits or legal purposes. This proactive approach to compliance can help organisations avoid costly penalties and reputational damage associated with non-compliance.
What cost savings can businesses expect from ILM?
Implementing an effective ILM strategy can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By optimising storage resources and implementing tiered storage solutions, organisations can reduce their overall storage costs, allocating expensive, high-performance storage only to data that truly requires it. ILM also helps identify and remove unnecessary data, reducing storage requirements and associated costs.
Furthermore, by improving data accessibility and management, ILM can lead to increased operational efficiency, reducing the time and resources spent on data-related tasks. The improved compliance and risk management aspects of ILM can also result in cost savings by helping organisations avoid fines and legal issues related to improper data handling or retention.
In the long term, these combined benefits can translate into substantial cost reductions and improved return on investment for an organisation’s data management efforts.
How does Information Lifecycle Management handle unstructured data?
Unstructured data, which includes documents, emails, images, and other content that doesn’t fit neatly into traditional database structures, presents unique challenges for Information Lifecycle Management. However, effective ILM strategies must address this type of data, as it often comprises a significant portion of an organisation’s information assets.
What challenges does unstructured data pose for ILM?
Unstructured data poses several challenges for ILM due to its diverse nature and lack of standardised format. Unlike structured data, which can be easily categorised and managed within databases, unstructured data is often scattered across various storage systems and formats. This makes it difficult to apply consistent management policies and to track the data’s lifecycle effectively.
Additionally, the sheer volume of unstructured data generated by modern organisations can overwhelm traditional storage and management systems. Another significant challenge is the difficulty in automatically classifying and assigning value to unstructured data, as its importance may not be immediately apparent without human intervention. These factors combined make it crucial for organisations to develop specific strategies within their ILM framework to address the unique characteristics of unstructured data.
Which tools can help manage unstructured data in ILM?
To effectively manage unstructured data within an ILM strategy, organisations can leverage various tools and technologies. Content management systems (CMS) and enterprise content management (ECM) platforms can help organise and manage diverse types of unstructured data, providing features for classification, retention, and access control.
File analysis tools can scan unstructured data repositories to identify redundant, obsolete, or trivial information, aiding in data cleanup and storage optimisation. Data discovery and classification tools use machine learning and pattern recognition to automatically categorise unstructured data based on its content and context.
Additionally, data governance platforms can help enforce policies and track the lifecycle of unstructured data across various systems. By integrating these tools into their ILM strategy, organisations can better manage the complexities of unstructured data throughout its lifecycle.
How does metadata play a role in managing unstructured data?
Metadata plays a crucial role in managing unstructured data within an ILM framework. By attaching descriptive information to unstructured data files, metadata provides context and enables more effective classification, search, and management of these diverse information assets. In the context of ILM, metadata can include information such as creation date, author, last modified date, file type, and custom tags that describe the content or business value of the data.
This metadata can be used to automate classification processes, apply appropriate retention policies, and facilitate more accurate search and retrieval of unstructured data. Moreover, metadata can help track the lifecycle stages of unstructured data, enabling organisations to implement appropriate management actions as the data moves through different phases of its lifecycle. By leveraging metadata effectively, organisations can bring structure to their unstructured data, making it more manageable within their overall ILM strategy.
Mastering Every Phase of Your Information’s Journey
Information moves through various stages during its lifecycle, from initial creation to secure disposal. Mastering each phase is crucial for maintaining data integrity, compliance, and efficiency.
Trust Crown Information Management to guide you in mastering every phase of your information’s journey, empowering your organization with seamless control and reliability.
What are the best practices for implementing Information Lifecycle Management?
Implementing an effective Information Lifecycle Management strategy requires careful planning and adherence to best practices. By following these guidelines, organisations can ensure that their ILM initiatives align with business objectives, comply with regulatory requirements, and maximise the value of their information assets throughout the data lifecycle.
How should businesses approach data classification in ILM?
Data classification is a fundamental component of any successful ILM strategy. Businesses should approach this process by first establishing a clear and consistent classification scheme that aligns with their organisational needs and regulatory requirements. This typically involves categorising data based on factors such as sensitivity, business value, and legal retention requirements.
It’s important to involve stakeholders from various departments, including legal, compliance, and business units, to ensure that the classification scheme accurately reflects the organisation’s data landscape. Automated tools can be employed to assist with initial classification, but human oversight is often necessary to refine and validate the results. Regular reviews and updates of the classification scheme are essential to ensure it remains relevant as business needs and regulatory landscapes evolve.
By implementing a robust data classification approach, organisations can more effectively manage their data throughout its lifecycle, applying appropriate policies and protections based on the data’s classification.
What role does data governance play in successful ILM?
Data governance plays a critical role in the success of Information Lifecycle Management initiatives. It provides the overarching framework that defines how data should be managed, accessed, and used within the organisation. A strong data governance program establishes clear policies, procedures, and responsibilities for data management, ensuring that ILM practices are consistently applied across the organisation.
This includes defining roles such as data owners, stewards, and custodians, who are responsible for overseeing different aspects of data management throughout its lifecycle. Data governance also helps ensure compliance with regulatory requirements by establishing and enforcing data handling and retention policies.
Moreover, it facilitates better decision-making around data management by providing a clear understanding of the organisation’s data assets and their value. By integrating data governance principles into their ILM strategy, organisations can create a more cohesive and effective approach to managing their information assets throughout the data lifecycle.
How does Information Lifecycle Management support data protection and security?
Information Lifecycle Management plays a crucial role in supporting data protection and security efforts within organisations. By providing a comprehensive framework for managing data throughout its lifecycle, ILM helps ensure that appropriate security measures are applied at each stage, from creation to deletion.
This holistic approach to data management enhances an organisation’s overall security posture and helps mitigate risks associated with data breaches, unauthorised access, and non-compliance with data protection regulations.
How does ILM help with data retention and deletion policies?
ILM plays a vital role in establishing and enforcing effective data retention and deletion policies. By categorising data based on its business value, legal requirements, and regulatory obligations, ILM enables organisations to apply appropriate retention periods to different types of information. This ensures that data is kept for as long as it’s needed, whether for operational, legal, or historical purposes and then securely deleted when it’s no longer required.
ILM frameworks typically include automated processes for moving data through different stages of its lifecycle, including archiving and deletion, based on predefined rules and policies. This automation helps reduce the risk of human error in retention and deletion processes, ensuring more consistent compliance with data protection regulations.
Can ILM improve disaster recovery and business continuity?
Information Lifecycle Management can significantly enhance an organisation’s disaster recovery and business continuity capabilities. By implementing a comprehensive ILM strategy, organisations gain a clear understanding of their data assets, their relative importance, and where they are stored throughout their lifecycle. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective disaster recovery plans that prioritise the protection and recovery of critical data.
ILM’s tiered storage approach also supports more efficient backup and recovery processes, as organisations can tailor their backup strategies based on the value and criticality of different data sets. For instance, mission-critical data might be replicated in real-time to a disaster recovery site, while less critical data might be backed up less frequently.
By adopting a comprehensive ILM approach, businesses can better manage their data assets, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency in their IT infrastructure.
 Bahrain
Bahrain  Cambodia
Cambodia